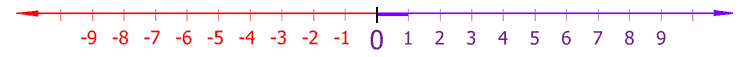Number line
In basic mathematics, a number line is a picture of a straight line on which every
point is assumed to correspond to a real number and every real number to a point.[1] Often the integers are shown as specially-marked points evenly
spaced on the line. Although this image only shows the integers from −9
to 9, the line includes all real numbers, continuing
"forever" in each direction, and also numbers not marked that are
between the integers. It is often used as an aid in teaching simple addition and subtraction, especially involving negative numbers.
It is divided into two symmetric halves by the origin, i.e. the number zero.
In advanced mathematics, the expressions real number line, or real line are typically used to indicate the above-mentioned
concept that every point on a straight line corresponds to a single real
number, and vice versa.
Drawing the number line ( see: http://www.khanacademy.org/video/locate-integers-on-a-number-line?playlist=Developmental%20Math
The number line is usually represented as being horizontal. Customarily, positive numbers lie on the right side of zero, and negative numbers lie on the left side of zero. An arrowhead on
either end of the drawing is meant to suggest that the line continues
indefinitely in the positive and negative real numbers, denoted by![]() .
The real numbers consist of irrational numbers and rational numbers, as well as the integers, whole numbers, and the natural numbers (the counting numbers).
.
The real numbers consist of irrational numbers and rational numbers, as well as the integers, whole numbers, and the natural numbers (the counting numbers).
A line drawn through the origin at right angles to the real
number line can be used to represent the imaginary numbers. This line, called imaginary line, extends the number line to a complex number plane, with points representing complex numbers.